Union Budget 2022-23 Important Highlights with PDF
The present finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget for 2022-23 on February 01, 2022. This post contains the most important points from this budget. The PDF for the same will be released soon.
Facts about Union Budget
- The Union Budget of India is also referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in Article 112 of the Constitution of India.
- It is presented on the First Day of February every year for the coming financial year. This trend started in the year 2017. Before 2017, Union Budget was presented on the last day of February. Also before 2017, Union Budget and Rail budget were presented separately and got merged from 2017.
- On 1 February 2021, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the first paperless budget.
- The first union budget of independent India was presented by R. K. Shanmukham Chetty on 26 November 1947.
Introduction to Budget 2022-23
- The total size of the budget 2022-23 is Rs 39.45 Lakh Crore. This figure also represents Total Receipt and Total expenditure as per the Budgeted Estimates for 2022-23. Total receipts other than borrowings in 2022-23 estimated at Rs. 22.84 lakh crore
- The total expenditure was projected at Rs. 34.83 lakh crore in the Budget Estimates 2021-22, which as per the Revised Estimate is now Rs. 37.70 lakh crore.
- Fiscal Deficit in 2022-23 is pegged at 6.4% of GDP. (Fiscal Deficit- Rs 16,61,196 crore.)
- Fiscal Deficit in current year: 6.9% of GDP (against 6.8% in Budget Estimates)
- Railway’s operating ratio pegged at 96.98% in 2022-23.
- The Centre has lowered the divestment target for fiscal 2022-23 to Rs 65,000 crore.
The budget 2022-23 lays a parallel track of two things:
| (1) Development durinf the next 25 years i.e blueprint for the Amrit Kaal – during the next 25 years | (2) Development after 100 years of Independence i.e big public investment
for modern infrastructure, readying for India at 100. |
| What is Amrit Kaal?- during the 75th Independence Day celebrations, PM Modi had unveiled a new roadmap for the country for the next 25 years, and termed it as ‘amrit kaal.’
It aims to better the lives of citizens, lessen the developmental divide between villages and cities, and reduce government interference in public life for the next 25 years – from India at 75 to India at 100. Three goals of Amrit Kaal: 1. Focus on growth and all inclusive welfare 2. Promoting technology enabled development, energy transition and climate action 3. Virtuous cycle starting from private investment, crowded in by public capital investment
|
i.e After this Amrit Kaal is over and India has completed 100 years of indepence.
This shall be guided by PM GatiShakti and be benefited by the synergy of multi-modal approach.
|
Four priorities of Budget 2022-23
1. PM GatiShakti
2. Inclusive Development
3. Productivity Enhancement & Investment, Sunrise Opportunities, Energy Transition and Climate Action
4. Financing of Investments
Priority 1: PM GatiShakti
The scope of PM GatiShakti National Master Plan will encompass the seven engines for economic transformation, seamless multimodal connectivity and logistics efficiency. These seven engines are: (1) Roads, (2) Railways, (3) Airports, (4) Ports, (5) Mass Transport, (6) Waterways, and (7) Logistics Infrastructure.
The scope of PM GatiShakti NMP will also include include the infrastructure developed by the state governments as per the GatiShakti Master Plan.
Important Points related to these seven engines:
Road Transport- PM GatiShakti Master Plan for Expressways will be formulated in 2022-23 to facilitate faster movement of people and goods.
The National Highways network will be expanded by 25,000 km in 2022-23.
Seamless Multimodal Movement of Goods and People- The data exchange among all mode operators will be brought on Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP).
Multimodal Logistics Parks- Contracts for implementation of Multimodal Logistics Parks at four locations through PPP mode will be awarded in 2022-23.
Railways- ‘One Station-One Product’ concept will be popularized to help local businesses & supply chains.
2,000 km of network will be brought under Kavach. Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) also known as Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system or ‘Kavach’ is a system to help the Railways to achieve the goal of “zero accidents”.
Four hundred new-generation Vande Bharat Trains will be developed and manufactured during the next three years.
One hundred PM GatiShakti Cargo Terminals for multimodal logistics facilities will be developed during the next three years.
New Scheme Annouced: Parvatmala Project: National Ropeways Development Programme
The aim of Parvatmala project is to improve connectivity and convenience in hilly areas for commuters, besides promoting tourism. This may also cover congested urban areas, where a conventional mass transit system is not feasible. Contracts for 8 ropeway projects for a length of 60 km will be awarded in 2022-23.
Priority 2: Inclusive Development
1. Development of Agriculture Sector- 2023 has been announced as the International Year of Millets.
Chemical-free Natural Farming will be promoted throughout the country, with a focus on farmers’ lands in 5-km wide corridors along river Ganga.
2. River Linking Projects like Ken Betwa project – Implementation of the Ken-Betwa Link Project, at an estimated cost of Rs. 44,605 crore will be taken up.
5 more such projects are under process of implementation- namely Damanganga-Pinjal, Par-TapiNarmada, Godavari-Krishna, Krishna-Pennar and Pennar-Cauvery
3. Development of MSME– Udyam, e-Shram, National Career Service Project (NCS) and Aatamanirbhar Skilled Employee-Employer Mapping (ASEEM) portals will be interlinked.
Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) will be extended up to March 2023 and its guarantee cover will be expanded by Rs. 50,000 crore to total cover of Rs. 5 lakh crore. This additional amount is earmarked exclusively for the hospitality and related enterprises.
[New Scheme] Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) programme – will be launched to help the MSME sector become more resilient, competitive and efficient. Outlay-Rs. 6,000 crore over 5 years.
4. Skill Development – The National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF) will be aligned with dynamic industry needs
[New Portal] Digital Ecosystem for Skilling and Livelihood – the DESH-Stack eportal – will be launched. This aims to empower citizens to skill, reskill or upskill through on-line training
Startups will be promoted to facilitate ‘Drone Shakti’ through varied applications and for Drone-As-A-Service (DrAAS).
5. Universalization of Quality Education- ‘one class-one TV channel’ programme of PM eVIDYA will be expanded from 12 to 200 TV channels.
In vocational courses, to promote crucial critical thinking skills, 750 virtual labs in science and mathematics, and 75 skilling e-labs for simulated learning environment, will be set-up in 2022-23.
6. National Tele Mental Health Programme- [New Scheme] A ‘National Tele Mental Health Programme’ will be launched to Improve the access to quality mental health counselling and care services. This will include a network of 23 tele-mental health centres of excellence. NIMHANS is the nodal centre and International Institute of Information Technology-Bangalore (IIITB) providing technology support.
7. Mission Shakti, Mission Vatsalya, Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0– Integrated architecture: Mission Shakti, Mission Vatsalya, Saksham Anganwadi, and Poshan 2.0 to be launched. Two lakh Anganwadis to be upgraded to Saksham Anganwadis.
8. Har Ghar, Nal Se Jal- Current coverage of Har Ghar, Nal Se Jal is 8.7 crores. Allocation of Rs. 60,000 crore has been made with an aim to cover 3.8 crore households in 2022-23.
9. Housing for All- In 2022-23, 80 lakh houses will be completed for the identified eligible beneficiaries of PM Awas Yojana, both rural and urban. Rs. 48,000 crore is allocated for this purpose
10. [New Scheme] Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PMDevINE)– PM-DevINE scheme will be implemented through the North-Eastern Council. It will fund infrastructure, and social development projects based on felt needs of the North-East. An initial allocation of Rs. 1,500 crore will be made.
11. Digital Banking by Post Offices: 100% of post offices to come on the core banking system
12. Digital Banking- Govt to set up 75 Digital Banking Units (DBUs) in 75 districts of the country by Scheduled Commercial Banks
Priority 3: Productivity Enhancement & Investment, Sunrise Opportunities, Energy Transition, and Climate Action
Ease of Doing Business 2.0 & Ease of Living to be launched
Green Clearances- A single window portal, PARIVESH, for all green clearances was launched in 2018. The scope of this portal will now be expanded, to provide information to the applicants.
The issuance of e-Passports using embedded chip and futuristic technology will be rolled out in 2022-23 to enhance convenience for the citizens in their overseas travel.
Land Record Management: States will be encouraged to adopt Unique Land Parcel Identification Number to facilitate IT-based management of records.
Centre for Processing Accelerated Corporate Exit (C-PACE) with process re-engineering, will be established to facilitate and speed up the voluntary winding-up of these companies from the currently required 2 years to less than 6 months.
The animation, visual effects, gaming, and comic (AVGC) sector– An AVGC promotion task force will be set-up to recommend ways for growth of AVGC sector and build domestic capacity for serving our markets and the global demand.
Support to 5G under PLI scheme- A scheme for design-led manufacturing will be launched to build a strong ecosystem for 5G as part of the Production Linked Incentive Scheme.
The contracts for laying optical fibre in all villages, including remote areas, will be awarded under the Bharatnet project through PPP in 2022-23. Completion is expected in 2025.
The Special Economic Zones Act will be replaced with a new legislation that will enable the states to become partners in ‘Development of Enterprise and Service Hubs’.
AtmaNirbharta in Defence– 68 per cent of the capital procurement budget will be earmarked for domestic industry in 2022-23, up from 58 per cent in 2021-22.
Solar Power- To facilitate domestic manufacturing for the ambitious goal of 280 GW of installed solar capacity by 2030, an additional allocation of Rs. 19,500 crore for Production Linked Incentive for manufacture of high efficiency modules, with priority to fully integrated manufacturing units from polysilicon to solar PV modules, will be made.
Priority 4: Financing of Investments
Outlay of Capital Expenditure: The outlay for capital expenditure in the Union Budget has been increased by 35.4 per cent from Rs. 5.54 lakh crore in the current year to Rs. 7.50 lakh crore in 2022-23. This outlay in 2022-23 will be 2.9 per cent of GDP.
Effective Capital Expenditure’ of the Central Government is estimated at Rs. 10.68 lakh crore in 2022-23, which will be about 4.1 per cent of GDP.
Digital Rupee: Digital Rupee will be issued by RBI using blockchain and other technologies, to be starting 2022-23. This will lead to efficient and cheaper currency management system.
The ‘Scheme for Financial Assistance to States for Capital Investment’– Outlay increased from Rs 10,000 crore to Rs 15,000 crore.
TAX PROPOSALS (Part-B)
Provision for Updated Income Tax Returns: The government to introduce a system where taxpayers can file an Updated Return on payment of additional tax. This updated return can be filed within two years from the end of the relevant assessment year. It will enable the assessee to declare income missed out earlier.
Tax for Cooperative societies- Alternate Minimum Tax paid by cooperatives brought down from 18.5 per cent to 15 per cent.
Surcharge on cooperative societies reduced from 12 per cent to 7 per cent for those having total income of more than Rs 1 crore and up to Rs 10 crores.
NPS for State Government Employee: Tax deduction limit increased from 10 per cent to 14 per cent on employer’s contribution to the NPS account of State Government employees.
Incentives for Start-ups- Period of incorporation of Start-ups extended by one year, up to 31.03.2023 for eligible start-ups to avail tax benefit. They get a tax incentive for three consecutive years out of ten years from incorporation.
Incentives under concessional tax regime– Last date for commencement of manufacturing or production under section 115BAB extended by one year i.e. from 31st March, 2023 to 31st March, 2024. Concessional tax regime of 15 per cent tax is given to newly incorporated domestic manufacturing companies.
Scheme for taxation of virtual digital assets- Any income from transfer of any virtual digital asset to be taxed at the rate of 30 per cent.
To capture the transaction details, TDS to be provided on payment made in relation to transfer of virtual digital asset at the rate of 1 per cent of such consideration above a monetary threshold.
Special Economic Zones- Customs Administration of SEZs to be fully IT driven and function on the Customs National Portal – shall be implemented by 30th September 2022.
Project imports and capital goods- National Capital Goods Policy, 2016 aims at doubling the production of capital goods by 2025.
It has been decided to phase out of the concessional rates in capital goods and project imports; and applying a moderate tariff of 7.5 percent. This will help in the growth of domestic sector and ‘Make in India’.
Gems and Jewellery- Customs duty on cut and polished diamonds and gemstones has been reduced to 5 per cent. Simply sawn diamond would attract nil customs duty. Customs duty of at least Rs 400 per Kg to be paid on imitation jewellery import.
Unblended fuel shall attract an additional differential excise duty of Rs. 2/litre from the 1st day of October 2022.
Budget Allocation to Major Scheme
| Scheme | Budget Allocation (2022-23 BE) |
| National Health Mission | Rs. 37,800 Crore |
| Jal Jeevan Mission | Rs. 60,000 Crore |
| National Education Mission | Rs. 39,553 Crore |
| Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana | Rs. 19,000 Crore |
| PM Kisan | Rs. 68,000 Crore |
| Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana | Rs. 6,400 Crore |
| Pardhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana | Rs. 10,000 Crore |
| Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme to Promote Telecom and Networking Products Manufacturing in India | Rs. 528 Crore |
| PLI for Large Scale Electronics and IT Hardware | Rs. 5,300 Crore |
Top 5 Ministry in terms of Budget Allocation for 2022-23 BE
| Ministry | Budget |
| Ministry of Defence | Rs. 5,25,166.15 Crore |
| Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution | Rs. 2,17,684.46 Crore |
| Ministry of Road Transport and Highways | Rs. 1,99,107.71 Crore |
| Ministry of Home Affairs | Rs. 1,85,776.55 Crore |
| Ministry of Railways | Rs. 1,40,367.13 Crore |
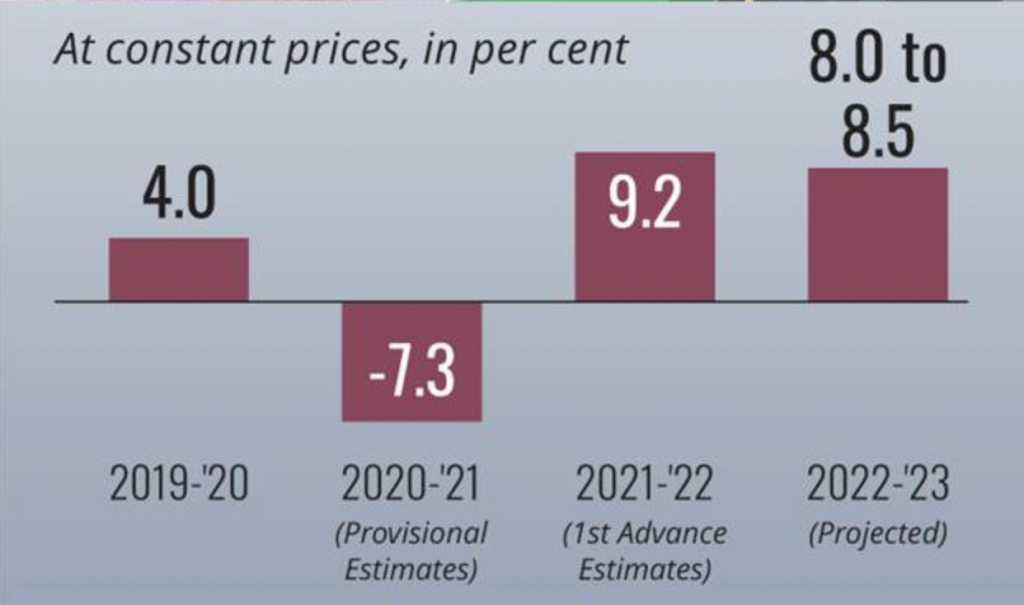
GDP Growth Rates in Budget 2022-23