The present finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Interim Union Budget for 2024-25 on February 01, 2024. This post contains the most important points from this budget.
Facts about Union Budget
- The Union Budget of India is also referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in Article 112 of the Constitution of India.
- It is presented on the First Day of February every year for the coming financial year. This trend started in the year 2017. Before 2017, Union Budget was presented on the last day of February. Also before 2017, Union Budget and Rail budget were presented separately and got merged from 2017.
- On 1 February 2021, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the first paperless budget.
- The first union budget of independent India was presented by R. K. Shanmukham Chetty on 26 November 1947.
What is Interim Budget
An interim budget is the budget presented by a government that is going through a period of transition by means of election. As the year 2024 will witness the election for central government, hence interim budget has been presented now. The full union budget will be presented after the elections.
Read about How is Interim Budget different from Full Budget?
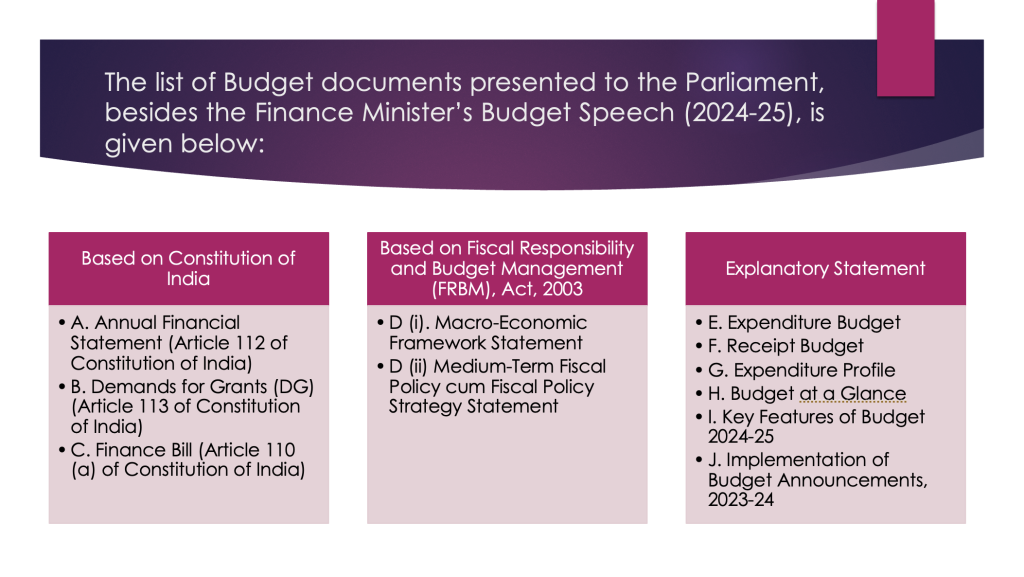
Key to Budget Document
Below we jump into the details of the interim union budget, let us see the important documents that form part of the union budget:
Vision of Interim Budget 2024-25: Prosperous Bharat in harmony with nature, modern infrastructure and opportunities for all.
Budget Estimate 2024-25
- Revenue Receipts= Rs. 30,01,275 Crore
- Capital Receipts= Rs. 17,64,494 Crore
- Total Receipts= Rs. 47,65,768 Crore (the total receipts other than borrowings are estimated at Rs. 30.80 Crore)
- Total Expenditure= Rs. 47,65,768 Crore (of which total capital expenditure is Rs. 11,11,111 crore)
- The scheme of fifty-year interest free loan for capital expenditure to states will be continued this year with total outlay of Rs. 1.3 lakh crore.
Deficit Statistics for 2024-25
- Fiscal Deficit = Rs. 16,85,494 Crore (5.1% of GDP)
- Revenue Deficit= Rs. 6,53,383 Crore (2% of GDP)
Revised Estimates (RE) 2023-24
- RE of the total receipts other than borrowings is Rs.27.56 lakh crore (of which the tax receipts are Rs.23.24 lakh crore)
- RE of the total expenditure is Rs.44.90 lakh crore.
- Revenue receipts at Rs.30.03 lakh crore are expected to be higher than the Budget Estimate, reflecting strong growth momentum and formalization in the economy.
- RE of the fiscal deficit is 5.8 per cent of GDP for 2023-24.
- The total capital expenditure in RE 2023-24 is estimated at Rs. 9,50,246 crore.
Highlights of the Interim Union Budget 2024-25
Here are the major topics touched on by the Finance Minister in Part A of the budget:
- Inclusive Development and Growth
- Social Justice
- Exemplary Track Record of Governance, Development and Performance (GDP)
- Strategy for ‘Amrit Kaal’
- Infrastructure Development
1. Inclusive Development and Growth
- The worries about food have been eliminated through free ration for 80 crore people
2. Social Justice
- Government is working to make India a ‘Viksit Bharat’ by 2047.
- Government to focus on four major castes: ‘Garib’ (Poor), ‘Mahilayen’ (Women), ‘Yuva’ (Youth) and ‘Annadata’ (Farmer).
2.1 Garib Kalyan, Desh ka Kalyan
- With the pursuit of ‘Sabka ka Saath’ in these 10 years, the Government has assisted 25 crore people to get freedom from multi-dimensional poverty.
- ‘Direct Benefit Transfer’ of Rs. 34 lakh crore from the Government using PM-Jan Dhan accounts has led to savings of
Rs. 2.7 lakh crore for the Government. - PM-SVANidhi has provided credit assistance to 78 lakh street vendors. From that total, 2.3 lakh have received credit for the third time.
- PM-JANMAN Yojana reaches out to the particularly vulnerable tribal groups, who have remained outside the realm of development so far.
- PM-Vishwakarma Yojana provides end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 trades.
2.2 Welfare of Annadata
- Every year, under PM-KISAN SAMMAN Yojana, direct financial assistance is provided to 11.8 crore farmers, including marginal and small farmers.
- Crop insurance is given to 4 crore farmers under PM Fasal Bima Yojana.
- Electronic National Agriculture Market has integrated 1361 mandis, and is providing services to 1.8 crore farmers with trading volume of Rs. 3 lakh crore.
2.3 Empowering Amrit Peedhi, the Yuva
- The Skill India Mission has trained 1.4 crore youth, upskilled and reskilled 54 lakh youth, and established 3000 new ITIs.
- PM ScHools for Rising India (PM SHRI) are delivering quality teaching, and nurturing holistic and well-rounded individuals.
- PM Mudra Yojana has sanctioned 43 crore loans aggregating to Rs. 22.5 lakh crore for entrepreneurial aspirations of our youth.
2.4 Momentum for Nari Shakti
- Thirty crore Mudra Yojana loans have been given to women entrepreneurs.
- Female enrolment in higher education has gone up by twenty-eight per cent in ten years.
- In STEM courses, girls and women constitute forty-three per cent of enrolment – one of the highest in the world.
- Over seventy per cent houses under PM Awas Yojana in rural areas to women as sole or joint owners have enhanced their dignity.
3. Exemplary Track Record of Governance, Development and Performance (GDP)
- Government is equally focused on a more comprehensive ‘GDP’, i.e., ’Governance, Development and Performance’.
- Average real income of the people has increased by fifty per cent.
4. Strategy for ‘Amrit Kaal’
- Aligning with the ‘Panchamrit’ goals, Government will facilitate sustaining high and more resource-efficient economic growth.
4.1 PM Awas Yojana (Grameen)
- Despite the challenges due to COVID, implementation of PM Awas Yojana (Grameen) is close to achieving the target of three crore houses.
- Two crore more houses will be taken up in the next five years to meet the requirement arising from increase in the number of families.
4.2 Rooftop solarization and muft bijli
- Through rooftop solarization, one crore households will be enabled to obtain up to 300 units free electricity every month.
- Each household is expected to save Rs.15000 to Rs.18000 annually.
4.3 Cervical Cancer Vaccination
- The government will encourage vaccination for girls in age group of 9 to 14 years for prevention of cervical cancer.
4.4 Maternal and child health care
- The newly designed U-WIN platform for managing immunization and intensified efforts of Mission Indradhanush will be rolled out expeditiously throughout the country.
4.5 Ayushman Bharat
- Healthcare cover under Ayushman Bharat scheme will be extended to all ASHA workers, Anganwadi Workers and Helpers.
4.6 Agriculture and food processing
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana has benefitted 38 lakh farmers and generated 10 lakh employment.
- Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Yojana has assisted 2.4 lakh SHGs and sixty thousand individuals with credit linkages.
4.7 Dairy Development
- India is the world’s largest milk producer but with low productivity of milch-animals.
- A comprehensive programme for supporting dairy farmers will be formulated and will be built on the success of existing schemes such Rashtriya Gokul Mission, National Livestock Mission, and Infrastructure Development Funds for dairy processing and animal husbandry.
4.8 Matsya Sampada
- Setting up of a separate Department for Fisheries has resulted in doubling of both inland and aquaculture production.
- Seafood export since 2013-14 has also doubled.
- Implementation of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) will be stepped up to:
(1) enhance aquaculture productivity from existing 3 to 5 tons per hectare,
(2) double exports to Rs. 1 lakh crore and
(3) generate 55 lakh employment opportunities in near future. - Five integrated aquaparks will be setup.
4.9 Lakhpati Didi
- Nearly one crore women have become Lakhpati Didi already.
- It has been decided to enhance the target for Lakhpati Didi from 2 crore to 3 crore
4.10 Research and Innovation for catalyzing growth, employment and development
- A corpus of rupees one lakh crore will be established with fifty-year interest free loan. The corpus will provide long-term financing or refinancing with long tenors and low or nil interest rates.
- A new scheme will be launched for strengthening deep-tech technologies for defence purposes and expediting ‘atmanirbharta’.
5. Infrastructure Development
- Capital expenditure outlay for Infrastructure development and employment generation to be increased by 11.1 per cent to Rs.11,11,111 crore, that will be 3.4 per cent of the GDP.
5.1 Railways
- Three major economic railway corridor programmes will be implemented. These are:
(1) energy, mineral and cement corridors,
(2) port connectivity corridors, and
(3) high traffic density corridors.
The projects have been identified under the PM Gati Shakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity. - Forty thousand normal rail bogies will be converted to the Vande Bharat standards to enhance safety, convenience and comfort of passengers.
5.2 Aviation Sector
- Number of airports have doubled to 149.
- Five hundred and seventeen new routes are carrying 1.3 crore passengers.
- Indian carriers have pro-actively placed orders for over 1000 new aircrafts.
5.3 Green Energy
- Government is commitment for ‘net-zero’ by 2070.
- Coal gasification and liquefaction capacity of 100 MT will be set up by 2030.
- Phased mandatory blending of compressed biogas (CBG) in compressed natural gas (CNG) for transport and piped natural gas (PNG) for domestic purposes will be mandated.
5.4 Promoting Investments
- FDI inflow during 2014-23 of USD 596 billion was twice of the inflow during 2005-14.
5.5 Reforms in the States for ‘Viksit Bharat’
- A provision of seventy-five thousand crore rupees as fifty-year interest free loan is proposed this year to support those milestone-linked reforms by the State Governments.
Here are the major topics touched on by the Finance Minister in Part B of the budget:
Direct Taxes
- Over the last ten years, the direct tax collections have more than trebled and the return filers swelled to 2.4 times.
- Average processing time of returns has been reduced from 93 days in the year 2013-14 to a mere ten days this year, thereby making refunds faster.
Indirect Taxes
- According to a recent survey conducted by a leading consulting firm, 94 per cent of industry leaders view the transition to GST as largely positive. According to 80 per cent of the respondents, it has led to supply chain optimisation, as elimination of tax arbitrage and octroi has resulted in disbanding of check posts at state and city boundaries.
- At the same time, tax base of GST more than doubled and the average monthly gross GST collection has almost doubled to ₹1.66 lakh crore, this year.
- As a result of number of steps in Customs to facilitate international trade import release time has declined:
- by 47 per cent to 71 hours at Inland Container Depots,
- by 28 per cent to 44 hours at air cargo complexes and
- by 27 per cent to 85 hours at sea ports
Tax Proposals
- Tax benefits to Start-Ups, investments made by Sovereign wealth funds or pension funds extended to 31.03.2025
- Tax exemption on certain income of IFSC units extended by a year to 31.03.2025 from 31.03.2024
- Government to withdraw:
- Outstanding direct tax demands upto Rs 25000 pertaining to the period upto FY 2009-10
- Outstanding direct tax demands upto Rs 10000 for financial years 2010-11 to 2014-15
This will benefit one crore tax payers
Tax rationalization efforts over the years
- No tax liability for income upto Rs 7 lakh, up from Rs 2.2 lakh in FY 2013-14
- Presumptive taxation threshold for retail businesses increased to Rs 3 crore from Rs 2 crore
- Presumptive taxation threshold for professionals increased to Rs 75 lakh from Rs 50 lakh
- Corporate income tax decreased to 22% from 30% for existing domestic companies
- Corporate income tax rate at 15% for new manufacturing companies
Budget Allocation for Specific Ministries
- Ministry of Defence – Rs. 6.2 Lakh Crore
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways – Rs. 2.78 Lakh Crore
- Ministry of Railways – Rs. 2.55 Lakh Crore
- Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution – Rs. 2.13 Lakh Crore
- Ministry of Home Affairs – Rs. 2.03 Lakh Crore
Budget Allocation to Major Schemes (2024-25)
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme = Rs. 86,000 Crore
- Ayushman Bharat-PMJAY = Rs. 7,500 Crore
- Production Linked Incentive Scheme = Rs. 6,200 Crore
- Modified Programme for Development of Semiconductors and display manufacturing ecosystem = Rs. 6,903 Crore
- Solar Power (Grid) = Rs. 8,500 Crore
- National Green Hydrogen Mission = Rs. 600 Crore